Rainwater, major alternative resource
The retention obligation
The regulation requires the retention of storm water above a certain flow to limit the risk of flooding. This graceful retention takes place through various techniques. AQUAE offers the best choices to meet the needs of large volumes.
Examples of retention tanks
Prefabricated HDPE tank (up to 66 m³)

Steel tank (up to 120 m³), with integrated filtration
 |
 |
| Example of storm water management system of a school group: The two tanks are twinned and sized for storm buffer (100 m3) and the storage of roof rainwater (40 m3 with integrated filtration) for watering green spaces. | |
Monobloc concrete tank that can be twinned
 |
 |
| Installation of a tank of 15 m3 (9 tons) | Twinning of two tanks of 15 |
 |
 |
| Installation of prefabricated components | Underground concrete tanks 180 m3 |
Easily accessible underground retention or infiltration modules
Our chamber systems are particularly adapted to large volumes and have many advantages.
- Uses: to create a storm buffer tank, an infiltration basin, or a pool for rainwater to be reused (These three functions can be combined);
- The specially designed shapes of the chambers give them exceptional resistance, thus they can be installed under roads opening to all types of vehicles, including fire-fighting lanes. (CSTB-CSTBAT technical opinion);
- The joint use of chambers and calibrated pebbles ensures long-term structural reliability and eliminates the risk of compaction or collapse due to material creep;
- The chambers are easily accessible and cleanable; The smallest pieces accumulated over time can be evacuated in order to maintain best performance;
- A simple and quick installation is made possible thanks to the lightness of chambers (installation of 100m3 per day by two people - excluding excavation and laying of membrane).
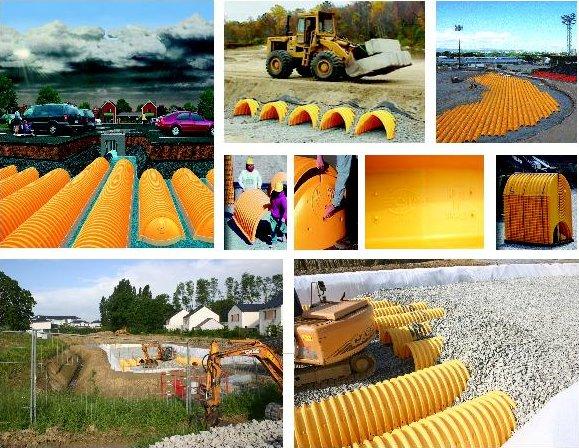 |
| Example of implementation of a 300 m3 chamber to replace an open-air storm basin at the centre of a town site, which was considered unsafe, unsightly and was causing nuisances (mosquitoes, unpleasant odours). Once completed, the site will be converted into public park with games for children (Nantes). |
Rainwater infiltration modules.
Become mandatory in the local urban planning scheme of many communes, or in the regulation of the majority of new developments, they replace the traditional centralized infiltration systems (type of pump).
The specially designed shapes of the chambers give them exceptional resistance, thus they can be installed under roads opening to all types of vehicles, including fire-fighting lanes. (CSTB-CSTBAT technical opinion);
The installation by a single person is made possible thanks to the lightness of the chambers (10 kg), which are fixed to one another by a simple clip. No glue, no tool or large gear are needed. The installation of the chambers allows large radii of curvature, which make it possible to avoid and go around obstacles.
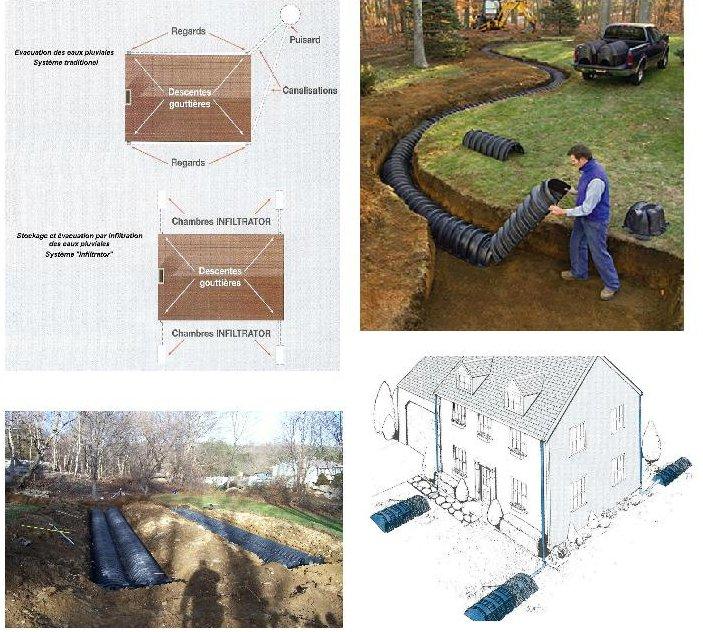
Creation of a blind room with desired volume in the basement of a building

Combine regulatory obligations with ecological and economic interests
The legislative retention obligation can be profitable by using water thus stored to cover certain needs of the related installations. Uses can be diverse: industrial process, toilet tank, surface cleaning, watering, fire reserves: supply of dry columns and sprinkler systems (costly weekly tests with city water).
The intervention of AQUAE from the stage of project conception makes it possible to absorb the cost of the work fulfilling regulatory obligations. The following diagram shows an example of a retention tank offering an integrated solution to this objective.
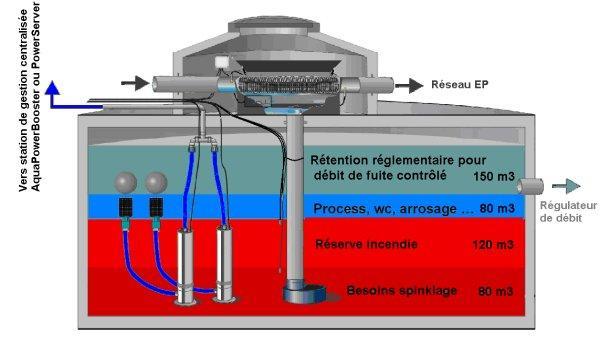
The sizing of a retention basin should firstly satisfy the regulatory aspects of rainstorms storage and discharge at controlled flow. In order to reduce the cost of installations and investments, it can then satisfy, in whole or in part, the technical water supply to cover various non-food, non-corporeal needs. There are many uses in the industry regarding process (non-food) water such as cleaning surfaces or rolling stock, cooling, demoulding, cutting and watering.
As for collective buildings, stored rainwater can be used for the supply of sanitary facilities, the watering of green areas, and also to form the fire reserves and supply the sprinkler networks.
Recovery of rainwater
The diagram below shows the general principle of a rainwater harvesting installation and its main components.
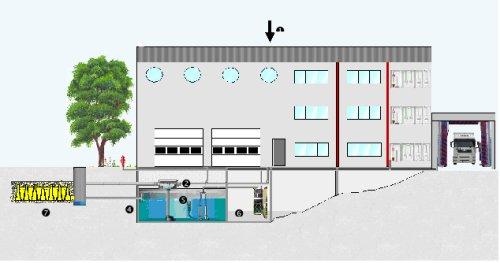 |
||
| (1) Collecting roof water | (2) Filtration before storage | (3) Arrival of water at the bottom of the tank avoiding the eddies |
| (4) Overflow siphon designed for the evacuation of floating substance | (5) Suction under water surface | (6) Management station supplying the needs: sanitary facilities, faucet, process water, fire reserves |
| (7) System of reservoir modules designed for retention or infiltration | ||

 Photovoltaic, biomass, biogas, geothermal, these green sectors are multiplying and diversifying. Do these sectors work well?
Photovoltaic, biomass, biogas, geothermal, these green sectors are multiplying and diversifying. Do these sectors work well? Aquae Environnement equips Carpe Diem tower at la Défense by ensuring the recycling of rainwater from facades and greywater from washbasins.
Aquae Environnement equips Carpe Diem tower at la Défense by ensuring the recycling of rainwater from facades and greywater from washbasins. Aquae Environnement equips the new headquarters of Bouygues TELECOM by ensuring water supply of 350 toilets on 23 levels and the supply of the system of green spaces watering!
Aquae Environnement equips the new headquarters of Bouygues TELECOM by ensuring water supply of 350 toilets on 23 levels and the supply of the system of green spaces watering! Aquae Environnement equips the new stadium of Nice with rainwater recycled from the 30,000 square meter roof to supply sanitary facilities and fire network as well as to water the lawn.
Aquae Environnement equips the new stadium of Nice with rainwater recycled from the 30,000 square meter roof to supply sanitary facilities and fire network as well as to water the lawn. Millions of cubic meters of water are wasted in France, because people have not yet form the habit of recovering rainwater.
Millions of cubic meters of water are wasted in France, because people have not yet form the habit of recovering rainwater.




